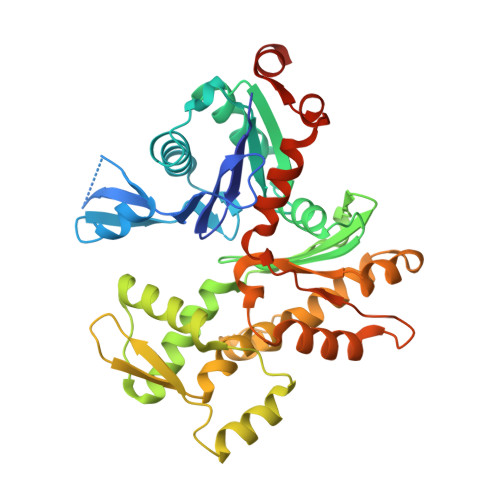
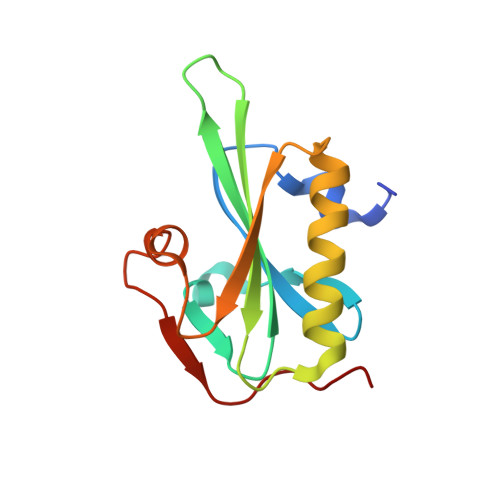
Atomic view into Plasmodium actin polymerization, ATP hydrolysis, and fragmentation.
Kumpula, E.P., Lopez, A.J., Tajedin, L., Han, H., Kursula, I.(2019) PLoS Biol 17: e3000315-e3000315
- PubMed: 31199804
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000315
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6I4D, 6I4E, 6I4F, 6I4G, 6I4H, 6I4I, 6I4J, 6I4K, 6I4L, 6I4M - PubMed Abstract:
Plasmodium actins form very short filaments and have a noncanonical link between ATP hydrolysis and polymerization. Long filaments are detrimental to the parasites, but the structural factors constraining Plasmodium microfilament lengths have remained unknown. Using high-resolution crystallography, we show that magnesium binding causes a slight flattening of the Plasmodium actin I monomer, and subsequent phosphate release results in a more twisted conformation. Thus, the Mg-bound monomer is closer in conformation to filamentous (F) actin than the Ca form, and this likely facilitates polymerization. A coordinated potassium ion resides in the active site during hydrolysis and leaves together with the phosphate, a process governed by the position of the Arg178/Asp180-containing A loop. Asp180 interacts with either Lys270 or His74, depending on the protonation state of the histidine, while Arg178 links the inner and outer domains (ID and OD) of the actin protomer. Hence, the A loop acts as a switch between stable and unstable filament conformations, the latter leading to fragmentation. Our data provide a comprehensive model for polymerization, ATP hydrolysis and phosphate release, and fragmentation of parasite microfilaments. Similar mechanisms may well exist in canonical actins, although fragmentation is much less favorable due to several subtle sequence differences as well as the methylation of His73, which is absent on the corresponding His74 in Plasmodium actin I.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biocenter Oulu and Faculty of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland.