Structure guided functional analysis of the S. cerevisiae Mre11 complex.
Petrini, J., Hohl, M., Yu, Y., Kuryavyi, V., Patel, D.(2024) Res Sq
- PubMed: 39711558
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-5390974/v1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9BI4 - PubMed Abstract:
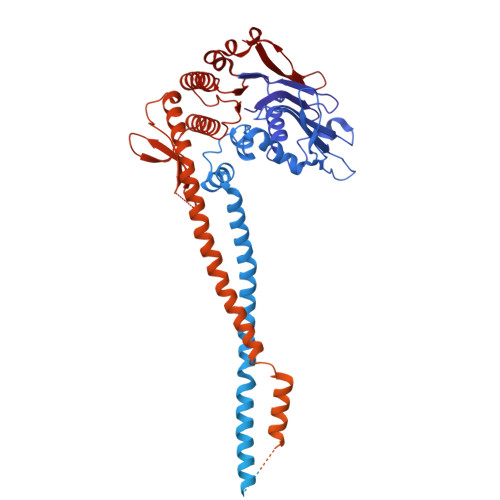
The Mre11 complex comprises Mre11, Rad50 and Nbs1 (Xrs2 in S. cerevisiae ). The core components, Mre11 and Rad50 are highly conserved, with readily identifiable orthologs in all clades of life, whereas Nbs1/Xrs2 are present only in eukaryotes. In eukaryotes, the complex is integral to the DNA damage response, acting in DNA double strand break (DSB) detection and repair, and the activation of DNA damage signaling. We present here a 3.2 Å cryo-EM structure of the S. cerevisiae Mre11-Rad50 complex with bound dsDNA. The structure provided a foundation for detailed mutational analyses regarding homo and heterotypic protein interfaces, as well as DNA binding properties of Rad50. We define several conserved residues in Rad50 and Mre11 that are critical to complex assembly as well as for DNA binding. In addition, the data reveal that the Rad50 coiled coil domain influences ATP hydrolysis over long distances.
Organizational Affiliation:
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.